DIN Rail Temperature Controllers: The Cornerstone of Precision Temperature Management
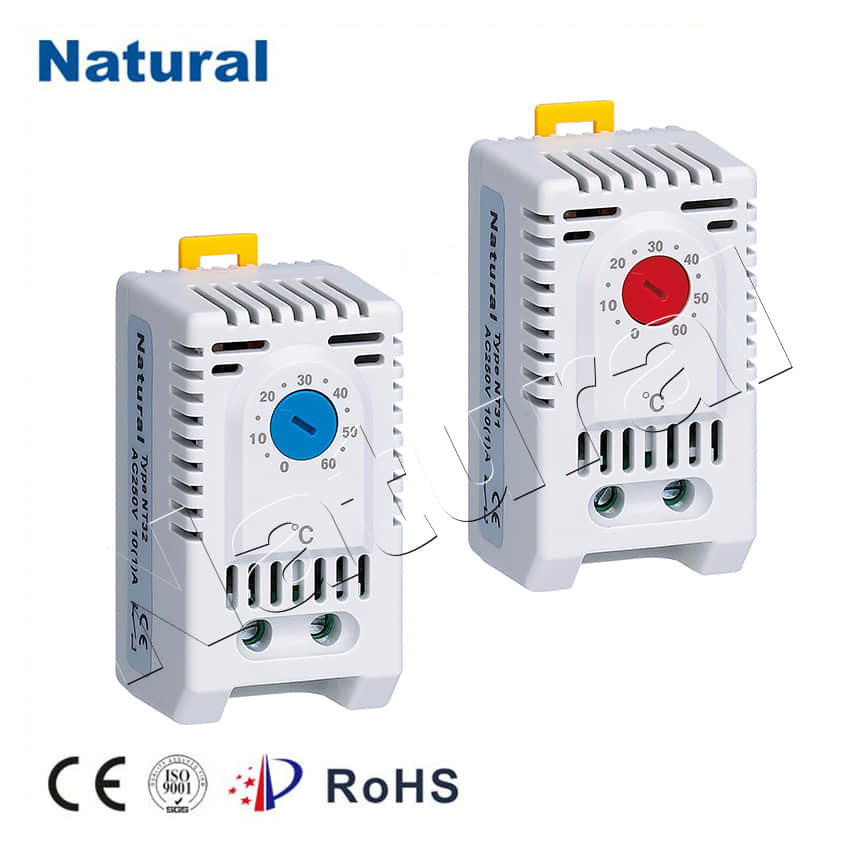

In the realm of industrial process control and automation, precise temperature regulation is often the key to success. Whether it's in manufacturing, food processing, or environmental control systems, maintaining the right temperature is crucial for product quality and process efficiency. One indispensable tool in achieving this precision is the DIN rail temperature controller. In this article, we will delve into the world of DIN rail temperature controllers, exploring their functionality, applications, and the benefits they offer. Understanding DIN Rail Temperature Controllers
DIN rail temperature controllers are compact, reliable devices designed to monitor and control temperature in various industrial and commercial applications. They are named after the DIN rail, a standardized mounting system widely used in electrical cabinets and control panels. This design allows for easy integration into existing control systems.
Versatility in Application
One of the standout features of DIN rail temperature controllers is their versatility. These controllers can be employed in a wide array of industries and scenarios, including:
Manufacturing:DIN rail temperature controllers are commonly used in manufacturing processes to ensure consistent product quality. They help regulate temperature in equipment like ovens, extruders, and molding machines.
Food Processing:In the food industry, precise temperature control is essential for food safety and quality. DIN rail controllers are used in ovens, refrigerators, and pasteurization systems.
HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning):DIN rail temperature controllers play a vital role in maintaining comfortable indoor environments. They regulate the temperature of heating and cooling systems, ensuring energy efficiency.
Laboratories:Laboratories often rely on these controllers for experiments that require specific temperature conditions, such as incubators, environmental chambers, and temperature-controlled baths.
Key Features and Advantages
DIN rail temperature controllers offer several key features and advantages, making them a preferred choice for temperature management:
Precision Control:These controllers provide accurate temperature control, often within fractions of a degree. This precision is vital in industries where temperature variations can impact product quality or safety.
Compact Design:Their compact size allows for easy installation in limited spaces, reducing the need for additional infrastructure.
Flexibility:DIN rail controllers can accommodate a variety of sensor inputs, including thermocouples, resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), and thermistors, making them adaptable to different temperature measurement needs.
User-Friendly Interface:Many models come with intuitive interfaces, enabling operators to set and monitor temperature parameters easily.
Alarm and Safety Features:These controllers often include alarms and safety features that can alert operators to temperature deviations or system malfunctions, minimizing downtime and potential product losses.
Remote Monitoring and Control:With the advancement of technology, many DIN rail controllers now offer remote monitoring and control capabilities, allowing operators to manage temperature settings from a distance, enhancing efficiency and convenience.
Conclusion
In the world of temperature regulation, DIN rail temperature controllers stand as indispensable tools, providing precision, versatility, and reliability. Their compact design and user-friendly interfaces make them accessible for various industries, from manufacturing to laboratory research. As technology continues to evolve, these controllers will likely play an even more significant role in achieving temperature control excellence, contributing to enhanced product quality, process efficiency, and energy conservation across diverse sectors.
 28 items Patent
28 items Patent
 28 items Patent
28 items Patent
 28 items Patent
28 items Patent