Bimetal Thermostats: A Marvel of Temperature Control Technology
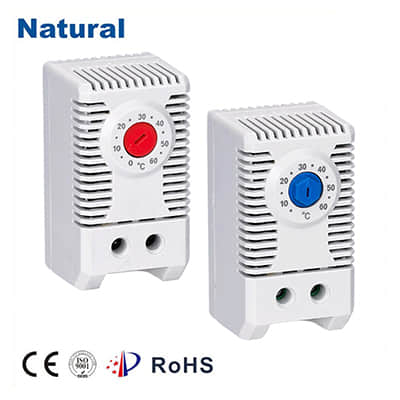

Temperature control is a critical aspect of various industrial, commercial, and domestic applications. Whether it's regulating the temperature in a home HVAC system, an oven, or a car engine, precision and reliability are paramount. One technology that has played a pivotal role in achieving this precision is the bimetal thermostat. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of bimetal thermostats, exploring their construction, working principle, applications, and advantages. What is a Bimetal Thermostat?
A bimetal thermostat is a temperature-sensitive device that employs the physical properties of two different metals to control temperature variations. These metals are typically bonded together and have different coefficients of thermal expansion. The most commonly used metal pair in bimetal thermostats are brass and steel, as they exhibit distinct thermal expansion characteristics.
How Do Bimetal Thermostats Work?
The fundamental principle behind a bimetal thermostat is based on the varying expansion rates of the two metals when exposed to temperature changes. When the temperature rises, the metals expand at different rates, causing the bonded strip to bend. Conversely, when the temperature drops, the strip returns to its original position. This bending and returning movement is harnessed to open or close an electrical circuit, controlling the connected device's heating or cooling elements.
Construction of Bimetal Thermostats
Bimetal Strip: The heart of a bimetal thermostat is its bimetallic strip, carefully selected to suit the desired temperature range. The choice of metals and their thickness determine the thermostat's sensitivity and accuracy.
Contact Points: At the ends of the bimetal strip, there are electrical contacts. When the strip bends, it causes these contacts to either touch (closing the circuit) or separate (opening the circuit).
Adjustment Mechanism: Many bimetal thermostats feature an adjustment mechanism that allows users to set the desired temperature range or differential.
Applications of Bimetal Thermostats
Bimetal thermostats find applications in a wide range of industries and everyday devices:
HVAC Systems: Bimetal thermostats are used in heating and cooling systems to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
Household Appliances: They are employed in ovens, refrigerators, water heaters, and irons to control heating elements.
Automotive Sector: Bimetal thermostats regulate engine temperature by controlling the flow of coolant.
Industrial Equipment: These thermostats ensure safe operating temperatures in industrial machinery.
Safety Devices: Bimetal thermostats are integral components in safety devices such as fire alarms and circuit breakers.
Advantages of Bimetal Thermostats
Accuracy: Bimetal thermostats provide precise temperature control, ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency.
Reliability: They are known for their durability and ability to withstand harsh environments.
Cost-Efficiency: Bimetal thermostats are cost-effective solutions for temperature control.
Low Power Consumption: They require minimal power to operate, making them suitable for battery-powered applications.
Quick Response: Bimetal thermostats respond rapidly to temperature changes, reducing temperature fluctuations.
In conclusion, bimetal thermostats are remarkable temperature control devices that have stood the test of time. Their ingenious construction and reliable operation make them indispensable in numerous industries and everyday appliances. As technology continues to advance, bimetal thermostats remain a vital component in our quest for precision temperature control, ensuring our comfort and safety in an ever-changing world.
 28 items Patent
28 items Patent
 28 items Patent
28 items Patent
 28 items Patent
28 items Patent