Introduction
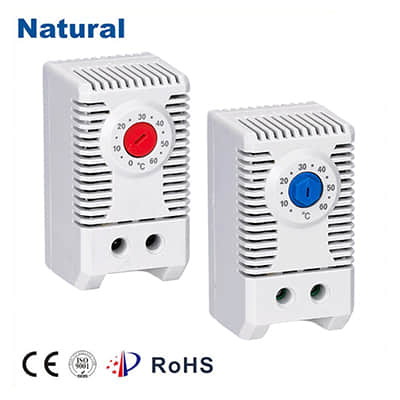

In the realm of temperature regulation, precision and efficiency are paramount. Bimetal thermostats have emerged as remarkable innovations that meet these criteria, offering an elegant solution for maintaining consistent temperatures across various applications. This article delves into the workings, applications, and advantages of bimetal thermostats, highlighting their role in modern technology and everyday life. The Inner Workings of Bimetal Thermostats
Bimetal thermostats operate based on the principle of differential expansion of two different metals. Typically, a bimetallic strip is composed of two layers of metals with distinct coefficients of thermal expansion, such as brass and steel. When exposed to temperature changes, these layers expand or contract at different rates, causing the strip to bend. This bending motion is harnessed to control electrical circuits that, in turn, regulate the heating or cooling mechanism.
Applications in Various Fields
Household Appliances:Bimetal thermostats are ubiquitous in household appliances like ovens, toasters, and refrigerators. In ovens, they ensure precise temperature control during baking, roasting, and broiling, contributing to evenly cooked meals. In refrigerators, bimetal thermostats help maintain optimal cooling levels, preserving food freshness.
HVAC Systems:Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems rely on bimetal thermostats to maintain desired indoor temperatures. The thermostats initiate heating or cooling cycles, enhancing energy efficiency and user comfort.
Automotive Industry:Bimetal thermostats play a vital role in regulating engine temperatures in automobiles. By controlling the flow of coolant between the engine and the radiator, these thermostats prevent overheating and ensure efficient engine operation.
Industrial Equipment:Industrial processes often require precise temperature control. Bimetal thermostats are used in equipment such as furnaces, kilns, and industrial dryers to ensure consistent and controlled heating, leading to improved product quality and reduced energy waste.
Advantages of Bimetal Thermostats
Reliability:Bimetal thermostats boast a simple and robust design that enhances their reliability. With fewer moving parts, there is less risk of mechanical failure, leading to longer lifespans and reduced maintenance costs.
Accuracy:The differential expansion of the bimetallic strip offers accurate temperature sensing and control. This precision ensures that the desired temperature is maintained within a narrow range, critical in applications where even slight deviations can have significant consequences.
Cost-Effectiveness:The manufacturing process of bimetal thermostats is cost-effective, making them an economical choice for various applications. Their longevity and low maintenance requirements further contribute to their cost-effectiveness.
Ease of Integration:Bimetal thermostats can be seamlessly integrated into complex systems due to their compact design and compatibility with electrical circuits. This adaptability makes them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Conclusion
Bimetal thermostats stand as a testament to the marriage of engineering ingenuity and scientific principles. Their ability to provide precise temperature control across numerous domains showcases their significance in modern technology. From household appliances to industrial machinery, these unassuming devices play a pivotal role in enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and reliability. As technology continues to evolve, bimetal thermostats will likely remain a cornerstone of temperature regulation, contributing to our comfort and quality of life.
 28 items Patent
28 items Patent
 28 items Patent
28 items Patent
 28 items Patent
28 items Patent