Introduction
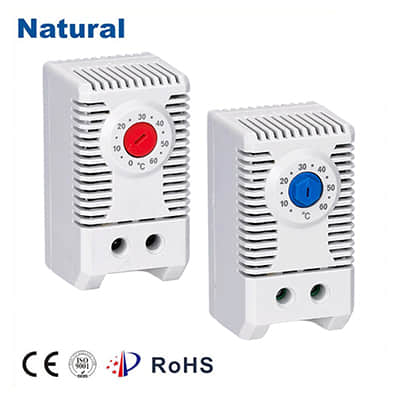

In the world of modern technology, temperature regulation plays a pivotal role in various applications. From household appliances to industrial processes, maintaining the right temperature is crucial for efficiency, safety, and performance. One of the remarkable innovations in this field is the bimetal thermostat – a device that combines simplicity with precision to achieve reliable temperature control. The Basics of Bimetal Thermostats
A bimetal thermostat is a temperature-sensitive device that operates based on the principle of thermal expansion of different metals. It consists of two strips of different metals, usually steel and copper, bonded together. These metals have different coefficients of thermal expansion, meaning they expand and contract at different rates when subjected to temperature changes.
Functioning
When the temperature around the bimetal thermostat changes, the two bonded metal strips respond differently, causing the entire strip to bend. This bending action is utilized to actuate a mechanical switch, which can either complete or interrupt an electrical circuit. In simple terms, when the temperature rises or falls beyond a certain set point, the bimetal thermostat triggers a response – like turning on or off a heating or cooling system.
Advantages of Bimetal Thermostats
Reliability: Bimetal thermostats are renowned for their reliability and durability. Since they consist of solid metal strips, they are not susceptible to wear and tear, making them ideal for long-term use.
Cost-Effective: These thermostats are cost-effective to produce, making them an economical choice for various applications. Their simple design and sturdy construction contribute to their affordability.
Accuracy: Bimetal thermostats offer a remarkable degree of accuracy in temperature control. Their response is consistent and repeatable, ensuring precise regulation of temperature.
Wide Range of Applications: From household appliances like ovens, to industrial machinery like boilers, bimetal thermostats find applications across various sectors due to their adaptability and reliability.
Safety: The inherent design of bimetal thermostats lends itself to safety features. They can be used to prevent overheating, which is crucial in scenarios where temperature regulation is critical for preventing accidents or equipment damage.
Limitations and Modern Advances
While bimetal thermostats offer many advantages, they do have some limitations. Their response time might be slower compared to electronic alternatives, and they can experience some hysteresis – a delay in switching back to the original state once the temperature stabilizes. However, modern engineering has led to improvements in these areas, minimizing their impact on performance.
Conclusion
In a world driven by technological advancements, the bimetal thermostat remains a steadfast solution for temperature regulation. Its simple yet effective design, coupled with its reliability and affordability, makes it a preferred choice in various applications. As technology continues to evolve, it's likely that bimetal thermostats will persist as an integral part of the temperature control landscape, serving both domestic and industrial needs with precision and efficiency.
 28 items Patent
28 items Patent
 28 items Patent
28 items Patent
 28 items Patent
28 items Patent