Introduction
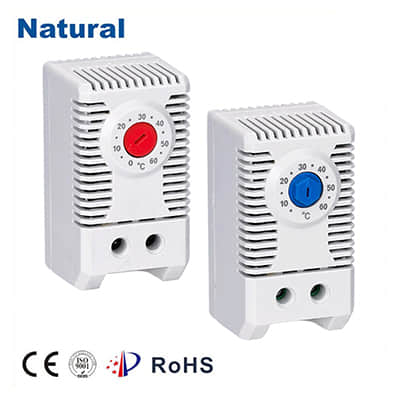

In the world of temperature regulation, bimetal thermostats stand as a remarkable embodiment of simplicity and efficiency. These devices, also known as bimetallic thermostats, have been an essential component in various industries, from home appliances to industrial machinery. This article explores the concept, working principle, applications, and advantages of bimetal thermostats, showcasing their significant role in modern temperature control systems. The Concept Behind Bimetal Thermostats
At its core, a bimetal thermostat is a temperature-sensitive switch composed of two distinct metal strips bonded together. The two metal strips have different coefficients of thermal expansion. This means that they expand or contract at different rates when exposed to changes in temperature. Typically, one strip expands more than the other when heated. This differential expansion causes the bonded strips to bend or warp, initiating a mechanical movement that triggers the switching action of the thermostat.
Working Principle
Bimetal thermostats operate on the principle of thermal expansion. When the temperature rises, the metal strip with the higher coefficient of expansion expands more, causing the bonded strip to bend towards that side. This bending action can be calibrated to a specific temperature range, allowing the thermostat to engage or disengage electrical contacts, thereby controlling the connected device or system.
Applications in Diverse Industries
Household Appliances:Bimetal thermostats are commonly found in everyday appliances like ovens, toasters, and refrigerators. In an oven, for instance, the thermostat ensures that the desired cooking temperature is maintained. As the oven heats up, the bimetal strip bends, disconnecting the heating element when the set temperature is reached and reconnecting it when the temperature falls.
HVAC Systems:Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems utilize bimetal thermostats to regulate indoor temperatures. These thermostats maintain a comfortable environment by turning on the heating or cooling system when the temperature deviates from the set point.
Automotive Applications:Bimetal thermostats are crucial in automotive engines to regulate the operating temperature. They help prevent overheating by controlling the flow of coolant through the engine.
Advantages of Bimetal Thermostats
Reliability:Bimetal thermostats are renowned for their robustness and reliability. The absence of complex electronics or sensors makes them less susceptible to electronic failures.
Cost-Effectiveness:The manufacturing process of bimetal thermostats is relatively simple, contributing to their cost-effectiveness, which is particularly important for applications requiring mass production.
Wide Temperature Range:These thermostats can be engineered to operate within a wide range of temperatures, making them versatile for various applications.
Conclusion
In the realm of temperature control technology, bimetal thermostats continue to demonstrate their indispensable value. Their ingenious design, based on the fundamentals of thermal expansion, has allowed them to maintain a pivotal role across industries. From household appliances to industrial machinery, the bimetal thermostat stands as a testament to the elegance of simplicity in engineering. As technology advances, these mechanical marvels will likely persist, adapting to new challenges and ensuring precise temperature regulation in a multitude of applications.
 28 items Patent
28 items Patent
 28 items Patent
28 items Patent
 28 items Patent
28 items Patent