the natural efficiency of differential thermostats
Release time:2025-08-25 00:49:48
A differential thermostat is an innovative and efficient temperature control system widely used in various applications such as heating, cooling, and energy regulation. Unlike traditional thermostats that regulate temperature based on a fixed value, a differential thermostat works by comparing two temperatures and activating the system when a specified temperature difference is reached. This unique method of temperature regulation allows for more natural, energy-efficient, and adaptive control. In this article, we will explore the natural advantages of differential thermostats, their working principles, and their applications.
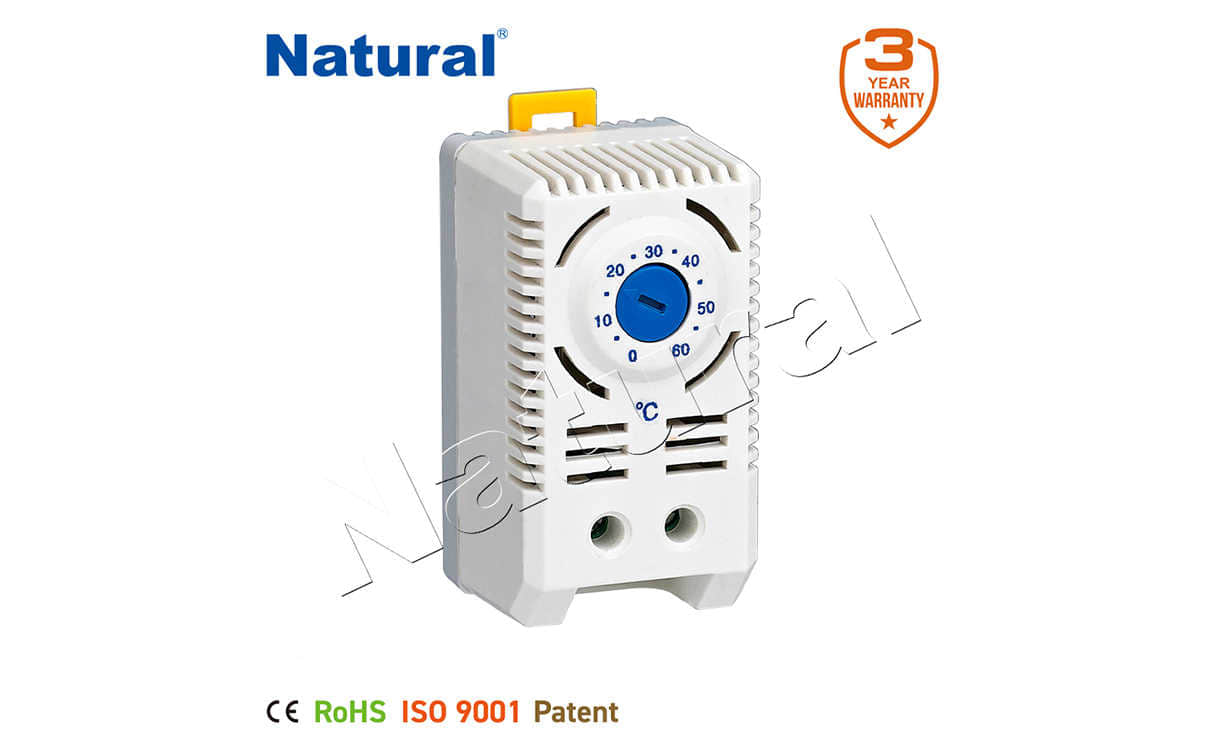

Working Principle of a Differential Thermostat
The core idea behind a differential thermostat is its ability to monitor and compare two different temperature points—one being the temperature of the environment or a specific location and the other being the temperature of a heat source or heat sink. When the difference between these temperatures exceeds a predetermined value, the thermostat activates or deactivates the heating or cooling system. For example, in solar water heating systems, a differential thermostat could compare the temperature of the water in the solar collector with the temperature of the water in the storage tank. If the collector water is warmer, the thermostat will trigger the pump to circulate the water and store the heat.


 28 items Patent
28 items Patent
 28 items Patent
28 items Patent
 28 items Patent
28 items Patent