understanding the functionality and applications of bimetal thermostat
Release time:2025-12-06 23:31:58
A bimetal thermostat is a type of temperature control device that operates based on the principle of two dissimilar metals expanding at different rates when heated. This simple yet effective mechanism has made bimetal thermostats a staple in many industries, from household appliances to automotive applications, and industrial temperature regulation systems. In this article, we will explore the working principle, design, benefits, and common uses of bimetal thermostats, offering a comprehensive overview of their role in temperature control.
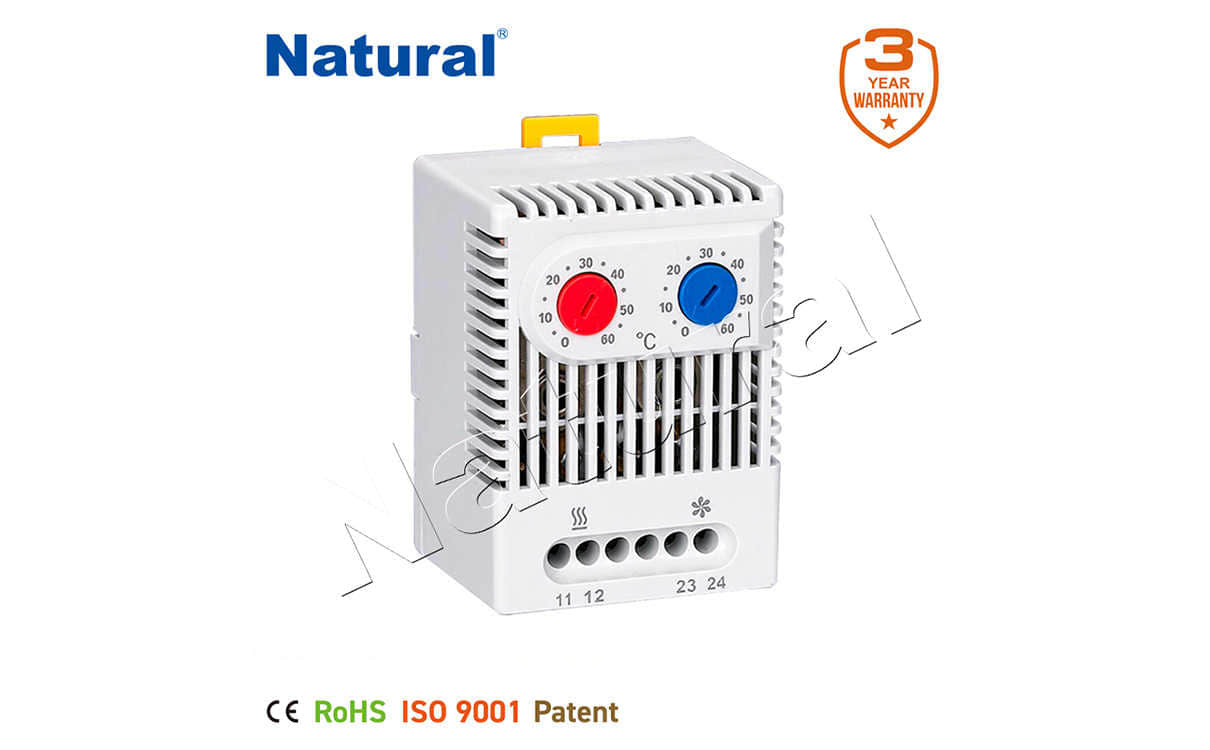

The Working Principle of Bimetal Thermostats
The core principle of a bimetal thermostat is the use of two metal strips with different coefficients of thermal expansion. These metals are typically chosen because they expand and contract at different rates when subjected to temperature changes. When the temperature rises or falls, the difference in expansion causes the bimetallic strip to bend or curve, which in turn activates a mechanical switch. This switch can either open or close the circuit, depending on the design, thus controlling the flow of electricity and regulating the temperature of the device or environment it is monitoring.


 28 items Patent
28 items Patent
 28 items Patent
28 items Patent
 28 items Patent
28 items Patent